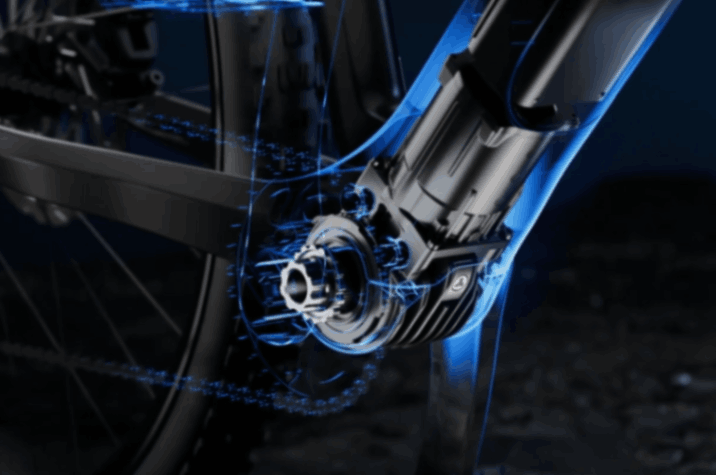
Motors
Electric bikes, or e-bikes, are simply bicycles with two key additional components: an electric motor and a battery. The motor and battery work together to provide assistance to the rider, making cycling easier and more efficient. In the UK, electric bikes must be 'pedal-assist' devices, meaning that the rider must turn the pedals when using the motor.
Basic Components
An electric bike includes all the standard bicycle parts such as:
- Wheels
- Tyres
- Gears
- Brakes
In addition to these, e-bikes have an electric motor and a battery.
E-bike motors
- The motor can be integrated into the frame between the pedals, driving the bike chain directly, or it could be located in one of the wheels.
- Electric motors are most efficient when spinning quickly, so they need to be geared down to work well on a bicycle.
- A mid-drive motor will have its own internal gears, plus the normal bike gears.
- Torque (or twisting effort - how hard the motor can push) is a key factor. Heavy bikes on hills need more torque than light bikes on the flat.
How electric bikes work
- Sensors: E-bikes are equipped with sensors that detect how quickly or how hard you are pedalling.
- Computer control: The sensors send information to the control circuitry and the software adjusts the power output of the motor to enhance your pedalling efforts. The more you pedal, the more assistance you receive from the motor. If you try to exceed the UK legal limit for electric bikes, the motor will cut out. You can go faster - such as when riding downhill - but the e-bike cannot assist you beyond the legal limit.
User Interface
E-bikes come with a display and controls, usually located on the handlebars or the frame. These provide key information and allow you to adjust settings:
- Display: Shows battery charge, speed, and other vital stats.
- Controls: Let you choose the level of motor assistance, from minimal help for slight inclines to maximum support for steep hills.
Many electric bikes also have a dedicated mobile phone app which will display battery charge status, speed and other data.
Key takeaways
- Motor position: E-bikes feature an electric motor located either in one of the wheels or as a central drive unit on the frame.
- Sensors and computer control: E-bikes are equipped with sensors that detect your pedalling speed or effort, and the computer adjusts the motor's power to assist you.
- Adjustable pedal assistance: Riders can choose different levels of motor assistance, from no or minimal help to significant support. Beyond the UK legal limit the rider gets no help.
If you'd like to find out more, read our comprehensive guide to motors.